
In the world of investing, uncertainty is the only certainty. Market swings, economic upheavals, and unforeseen global events can quickly shift the tides, leaving investors exposed to significant risks. For those seeking to mitigate downside risk while retaining the potential for upside gains, protective puts are a versatile tool worth exploring. This blog will delve into what protective puts are, how they work, and why they might be an excellent addition to your investment strategy.
What is a Protective Put?
A protective put is an options strategy where an investor purchases a put option on a stock they already own. This strategy acts as a form of insurance, providing the holder the right (but not the obligation) to sell the stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, within a specified time frame.
In essence, a protective put creates a floor for potential losses while allowing the investor to participate in any upside movement of the stock. It’s a classic example of risk management in action—hedging against adverse price movements while keeping the doors open for potential gains.
How Does a Protective Put Work?
To understand how a protective put functions, consider the following example:
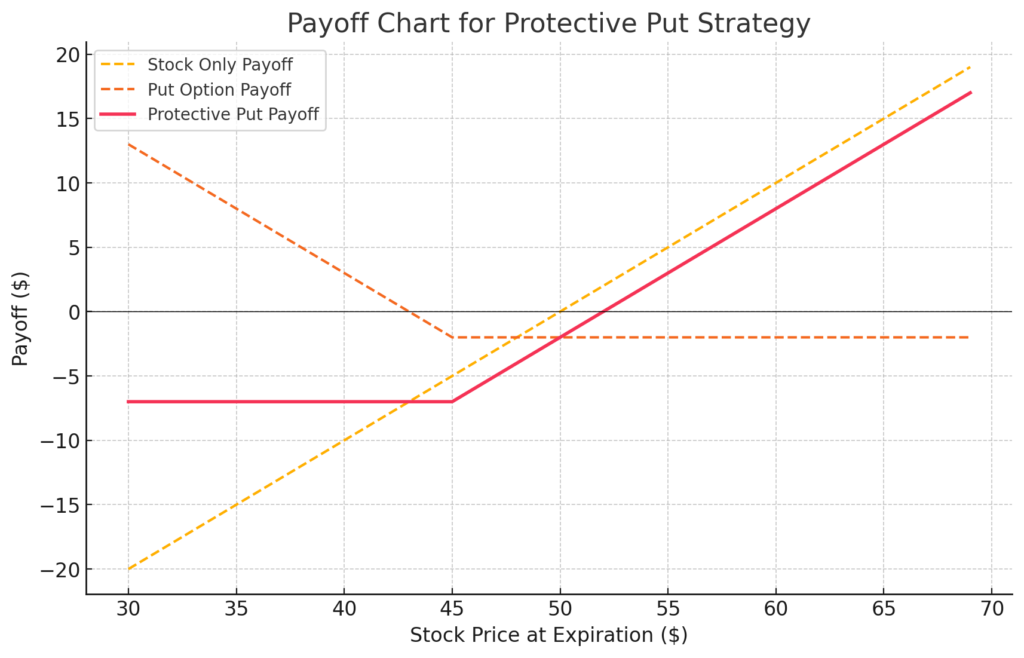
- The Stock Position: Suppose you own 100 shares of Company ABC, currently trading at $50 per share.
- The Put Option: To protect against downside risk, you purchase a put option with a strike price of $45, expiring in three months. The cost of the put option (the premium) is $2 per share.
- Stock Price Falls: If the stock price drops to $40, your put option gains value. You can exercise your right to sell the shares at $45, limiting your loss to $7 per share ($5 loss in stock value + $2 premium).
Possible Scenarios:
- Stock Price Falls: If the stock price drops to $40, your put option gains value. You can exercise your right to sell the shares at $45, limiting your loss to $7 per share ($5 loss in stock value + $2 premium).
- Stock Price Rises: If the stock price climbs to $60, your put option expires worthless. However, you still benefit from the $10 gain in stock value, reduced only by the $2 premium.
Advantages of Protective Puts
- Risk Management: Protective puts provide a safety net, limiting potential losses to a predetermined amount. This is especially valuable during periods of market volatility or when holding a concentrated position.
- Flexibility: Unlike stop-loss orders, which automatically sell your stock at a certain price, protective puts allow you to retain ownership. This is useful for long-term investors who want to avoid triggering taxable events.
- Participation in Upside Potential: Protective puts don’t cap your potential gains. If the stock price soars, you can let the put expire and enjoy the appreciation.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you have a hedge in place can alleviate the emotional stress of market fluctuations, helping you make more rational decisions.
Drawbacks of Protective Puts
- Cost: The premium paid for the put option represents a cost that can erode overall returns. Frequent use of protective puts can become expensive over time.
- Time Decay: Options lose value as they approach expiration, a phenomenon known as time decay. If the stock doesn’t move significantly, the put option may expire worthless, and the premium is lost.
- Opportunity Cost: The funds used to purchase the put option could have been invested elsewhere, potentially generating returns.
When to Use Protective Puts
Protective puts are not a one-size-fits-all solution but can be particularly effective in certain scenarios:
- Earnings Announcements: Stocks often experience significant price movements around earnings reports. A protective put can shield against downside surprises.
- Market Uncertainty: During periods of heightened market volatility or economic uncertainty, protective puts can act as a safeguard for your portfolio.
- Concentrated Positions: If you hold a large position in a single stock, a protective put can reduce the risk of substantial losses.
- Tax Considerations: For investors who want to avoid selling a stock and triggering capital gains taxes, protective puts offer an alternative way to manage risk.
Cost Management Strategies
The cost of protective puts can be a deterrent for some investors, but there are ways to manage this expense:
- Use Out-of-the-Money Puts: Buying a put with a strike price below the current stock price reduces the premium cost, though it also increases the potential loss before the hedge kicks in.
- Implement a Collar Strategy: Combine a protective put with a covered call (selling a call option on the same stock). The premium received from the call can offset the cost of the put.
- Time Your Purchase: Buy protective puts when implied volatility (a key determinant of option prices) is low.
Conclusion
Protective puts are a powerful tool in an investor’s arsenal, offering a way to balance risk and reward. While they come with costs and limitations, their ability to protect against significant losses while preserving upside potential makes them an attractive strategy for prudent investors.
As with any investment strategy, it’s essential to consider your individual goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation before implementing protective puts. By doing so, you can navigate market uncertainties with greater confidence, ensuring that your portfolio remains aligned with your long-term objectives.
By incorporating protective puts into your investment strategy, you not only safeguard your portfolio but also demonstrate a commitment to disciplined, thoughtful investing—qualities that can lead to sustained success in the ever-changing financial markets.
This article was written with the express intent for educational purposes only. Any examples used are in no way meant to be investment advice or recommendations. Options are leveraged financial products that entail significant risk. Always consult your financial advisor before taking any investment action.